A clearinghouse is a financial intermediary between buyers and sellers to make trading smooth and ensures that the parties adhere to their contractual obligations. Clearinghouses have a variety of roles and are essential to maintaining efficient markets. Because the clearinghouses are third parties, possessing securities in derivatives trading, there are always buyers to every seller and sellers for every buyer.
Clearinghouses are the backbone of the financial markets. Specifically, within the futures markets, they ensure that trades can be trustworthy, which offers stability.
How do clearinghouses work?
Clearinghouses work to create the most optimal market conditions. Responsibilities of clearinghouses include settling accounts, maintaining margin requirements of traders, and making sure traders actually pass along the respective securities to the other party. Clearinghouses are the middlemen of transactions, which reduces risk and eases the process of trading between multiple parties.
The most common market associated with clearinghouses is the futures market, because of the implied leverage associated with the financial products. The clearinghouses provide stability within potentially very volatile markets. Within each exchange exists a clearinghouse, which is mandated to close all transactions by the end of the trading days. Because of this, people trading must deposit funds into their accounts to maintain the margin requirements.
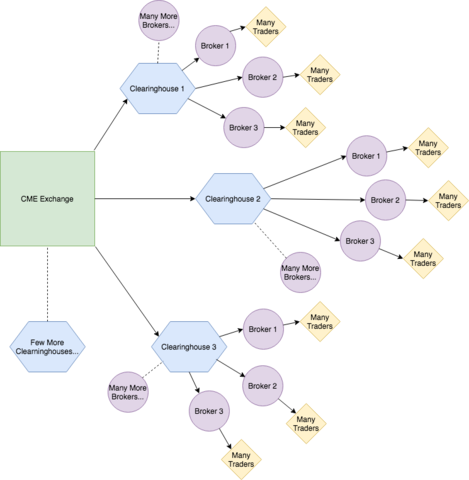
Example of clearinghouse at work
When a trader purchases a futures contract, the clearinghouse first must confirm that the trader has a large enough account balance to adhere to the margin requirements. The margin ensures that the trader will be able to hold the trade until it closes. Included within the initial margin requirements, traders must deposit maintenance margins while the trader’s account is open. In the event that the trader’s account balance drops below the margin requirements due to trading losses, the clearinghouse will request that the trader deposits additional funds into the account. This concept is known as a ‘margin call’. In order to ensure that the account does not collapse, the clearinghouse will close the account in the event that the trader cannot deposit more funds.
Margin calls protect traders because, without the clearinghouses regulation, there would nobody to protect the trades occurring. Clearinghouses provide the reassurance to traders that the counterparty will be able to support the transaction.
Clearinghouses are the foundation of trading, and provide the backing that traders need- they create efficiency, security, and build rapport of the exchanges.
Next article: What is Margin and How to Use it When Trading Futures