What are Futures and how do they work?
Futures contracts, also called futures, are legal agreements to buy or sell a specified quantity of an asset at a predetermined price at a time in the future. The contracts are standardized to the quality and quantity so that they can be traded on a futures exchange. Buying a futures contract takes on the obligation of buying the specified asset when the contract expires. Correspondingly the seller of the contract takes on the obligation to provide and sell the asset when the contract expires.
How do I get involved?
The futures market can be broken down into two categories of participants, hedgers and speculators. Hedgers are the ones that produce or purchase the asset to guarantee the price at which the asset will be sold or purchased for. Speculators are typically portfolio managers and traders that make bets based on the movement in the price of the underlying asset.
Why should I get involved?
Companies use futures contracts to lock in a price of a resource that they know they are going to need so that they don’t have the risks associated with fluctuations in price. For example, an airline company displays tickets on their website that are for sale 6 months prior to the trip. The company can’t know what the price of the fuel will be for the flight at that point. In order to ensure that they are able to purchase the fuel for what they anticipate it will cost they open a futures contract based on the specific price that they started selling the tickets for. This guarantees the price of fuel for the flight 6 months early and allows the company to minimize its risk.
But for the trader the benefit is the leverage. Most brokers only require 10% of the contract value before allowing you to place the trade. This exposes the trader to 10x the quantity and similarly 10x the profit. The reason for the 10% requirement is to give the broker safety in case the market doesn’t go in your favor.
A few other reasons to start trading futures is the liquidity and commissions. The futures market is extremely liquid due to the mass amount that is traded daily. This increased liquidity increases the likelihood that you will be able to buy or sell your contract at the price you want and the time you want. Commissions, which are set by brokers, are typically a fixed price that can range from $0.25 – $5 per side.
The futures market may involve assets but they are rarely physically exchanged. The market is typically just paper which means that most contracts are either settled or mention that no actual asset will be moved. Futures exist for trading stock exchange indexes, commodities, and currencies which shows the variability and diversity that exists in the market.
Conclusion
With the low requirements needed to open positions paired with the diversity, liquidity, and variability the futures market is primed for traders to benefit. By educating yourself and then taking it slow you can find that the futures market allows for profit as well as an understanding of the underlying market and its trends.
Related article about Futures Trading:
- Pros and Cons of Trading Futures
- What is the difference between trading options and futures – Options vs. Futures
- Clearinghouses and Trading
- What is Margin and How to Use it When Trading Futures
- De-risk your trading strategy using in the futures market using spreads
- How to Trade Futures With Small Accounts: Trading with E-Mini and E-Micro Futures
- 5 Fundamental Forces and Their Effects On the Futures Market
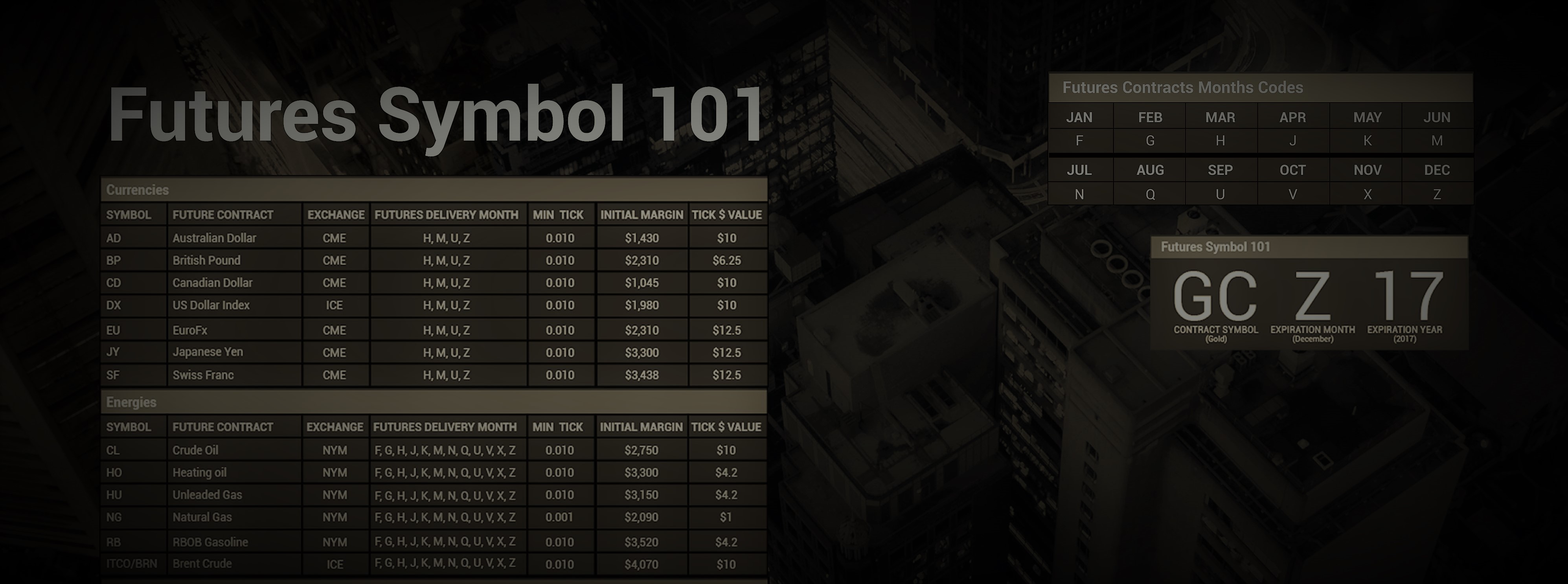
- Futures Symbols and Months